Keto Diet Meal Plan Simple: Easy Steps to Stay on Track
Keto Diet Meal Plan Simple: Easy Steps to Stay on Track
The Keto diet meal plan is a straightforward approach to achieving health goals like weight loss, increased energy, and better mental clarity. By focusing on high-fat, low-carb, and moderate-protein foods, this plan simplifies your journey into the ketogenic lifestyle. A well-structured Keto meal plan ensures you stay on track by guiding your food choices, managing macronutrient intake, and helping you achieve ketosis—the metabolic state where your body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Table of Contents
Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your diet, this guide offers simple steps to build and maintain a sustainable Keto diet meal plan. For additional tips, explore Keto Recipes – Ketogenic Diet to kickstart your journey.
What Is the Keto Diet?
The Keto diet, short for ketogenic diet, is a low-carb, high-fat eating plan that alters the way your body uses energy. Typically, the body relies on glucose from carbohydrates as its primary fuel source. However, the Keto diet significantly reduces carbohydrate intake, forcing the body to enter a metabolic state known as ketosis. In this state, the body burns fat for energy, producing molecules called ketones as a fuel source for the brain and muscles.
How the Keto Diet Works
- Carb Reduction: By limiting daily carb intake to 20–50 grams, the body depletes glycogen stores.
- Fat Adaptation: The body begins to metabolize fats into ketones, which replace glucose as the primary energy source.
- Protein Balance: Moderate protein intake prevents muscle loss while ensuring that excess protein doesn’t convert into glucose.
Benefits of Ketosis
- Fat Burning: Encourages the body to use stored fat for energy.
- Stable Energy Levels: Eliminates blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Improved Mental Clarity: Ketones provide a consistent and efficient energy source for the brain.
To better understand the science behind ketosis, check out Understanding Ketosis for in-depth insights.
Who Is the Keto Diet For?
The Keto diet is versatile and can benefit a wide range of individuals, including:
- Those seeking weight loss.
- People managing type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking for sustained energy.
- Individuals aiming to improve mental focus and reduce inflammation.
For a complete guide to starting your Keto journey, visit Introduction to the Keto Diet.
Benefits of Following a Keto Diet
The Keto diet is widely celebrated for its transformative health benefits. By shifting the body’s primary energy source from carbohydrates to fats, the diet unlocks a range of advantages that support weight management, energy stability, and overall well-being.
Weight Loss and Improved Energy
One of the most significant benefits of the Keto diet is its ability to promote fat loss while maintaining steady energy levels:
- Fat Burning: The body becomes highly efficient at burning stored fat, making the Keto diet particularly effective for targeting stubborn areas like the abdomen.
- Reduced Hunger: High-fat meals are more satiating, helping you feel full longer and reducing the temptation to snack.
- Consistent Energy: With stabilized blood sugar levels, you avoid the energy crashes associated with high-carb diets.
Explore Keto Recipes for Weight Loss for ideas to support your goals.
Enhanced Mental Clarity
The Keto diet has notable benefits for brain health:
- Ketones as Brain Fuel: Ketones provide a steady energy supply to the brain, leading to sharper focus and reduced brain fog.
- Neuroprotective Properties: Emerging research suggests that the Keto diet may support cognitive function and protect against neurological conditions.
For easy, brain-boosting meal ideas, check out Healthy Breakfast Recipes to start your day right.
Better Blood Sugar Control
The Keto diet is particularly beneficial for individuals managing blood sugar levels:
- Stabilized Glucose: By reducing carb intake, the diet prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes, creating a stable metabolic environment.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Studies have shown that the Keto diet can lower insulin resistance, making it an effective tool for managing type 2 diabetes.
For more information on meal options, visit Low-Calorie Lunch Ideas for diabetes-friendly dishes.
Other Benefits
- Reduced Inflammation: The high-fat, low-carb approach has been linked to decreased markers of inflammation in the body.
- Improved Heart Health: The inclusion of healthy fats like avocados and olive oil supports cholesterol management and cardiovascular health.
For a deeper understanding of how the Keto diet impacts your body, explore Tracking Progress on Keto to monitor your results effectively.
Understanding Macronutrients in the Keto Diet
The foundation of the Keto diet lies in balancing macronutrients—carbohydrates, fats, and proteins—in specific ratios to induce and maintain ketosis. Each macronutrient plays a distinct role in supporting the diet’s effectiveness and overall health benefits.
Carbohydrates: The Main Restriction
Carbs are drastically limited on the Keto diet, typically making up only 5-10% of daily caloric intake. This restriction forces the body to deplete glycogen stores and transition to burning fat for energy.
- Why Limit Carbs?
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. Reducing intake prompts the liver to produce ketones from stored fats, which become the alternative fuel. - Sources to Include: Focus on non-starchy vegetables like spinach, kale, broccoli, and zucchini for essential nutrients.
- Avoid These: Bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and high-carb fruits like bananas and apples.
For ideas on incorporating low-carb ingredients, visit Tasty Vegetable Recipes for creative meal inspiration.
Healthy Fats: The Powerhouse
Fats are the cornerstone of the Keto diet, comprising 70-75% of daily caloric intake. They provide the majority of energy while supporting ketosis.
- Why Focus on Fats?
Healthy fats promote satiety, enhance the flavor of meals, and are metabolized into ketones. - Best Sources:
- Oils: Coconut oil, olive oil, avocado oil.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds.
- Whole Foods: Avocados, fatty fish (like salmon), and cheese.
For more on incorporating fats effectively, check out Healthy Oils and Fats for Cooking.
Protein: The Balancing Act
Protein intake on Keto should be moderate, typically 20-25% of daily calories. Consuming too much protein can lead to gluconeogenesis, where excess protein is converted into glucose, potentially disrupting ketosis.
- Protein’s Role:
- Supports muscle maintenance and repair.
- Provides essential amino acids for overall health.
- Sources to Include: Eggs, poultry, fatty fish, grass-fed beef, and plant-based options like tofu and tempeh.
For high-protein meal ideas, visit High Protein Lunches for Work to ensure you meet your dietary needs without overdoing it.
The Ideal Macronutrient Ratio
To maintain ketosis:
- Fats: 70-75% of daily calories.
- Proteins: 20-25% of daily calories.
- Carbs: 5-10% of daily calories.
Understanding and tracking your macronutrient intake is key to Keto success. For tools to help monitor your progress, explore Apps and Tools for Tracking Macros for practical guidance.
Foods to Include and Avoid
Choosing the right foods is essential for maintaining ketosis and achieving success on the Keto diet. This section highlights the key foods you should include and those to avoid, helping you craft balanced, satisfying meals.
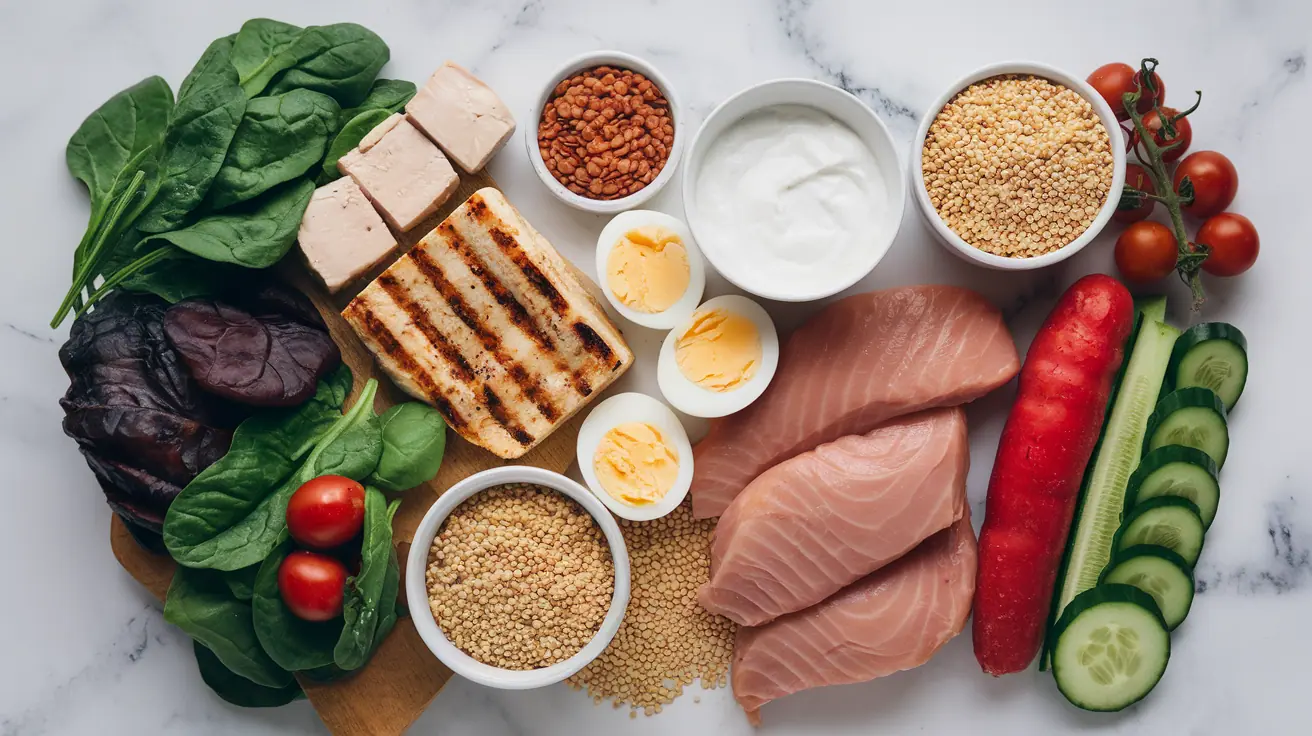
Foods to Include: Keto-Friendly Foods
The Keto diet emphasizes low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein foods that fuel your body for sustained energy and ketosis.
Low-Carb Vegetables
These vegetables are nutrient-dense and low in carbs, making them perfect for Keto:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, arugula, and Swiss chard.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage.
- Others: Zucchini, asparagus, bell peppers, and cucumbers.
Tip: Avoid starchy vegetables like potatoes and corn. For creative ideas, explore Tasty Vegetable Recipes.
Healthy Oils and Fats
Fats are the cornerstone of the Keto diet, and healthy fats are essential for energy and satiety:
- Plant-Based Fats: Avocado oil, coconut oil, and extra virgin olive oil.
- Animal-Based Fats: Butter, ghee, and lard.
- Whole Foods: Avocados, nuts (almonds, macadamia nuts), and seeds (chia seeds, flaxseeds).
For tips on using fats effectively, visit Healthy Oils and Fats for Cooking.
Protein Sources
Protein should be consumed in moderation to support muscle repair without disrupting ketosis:
- Meats: Grass-fed beef, pork, lamb, and chicken thighs.
- Seafood: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- Eggs: A versatile and affordable protein source.
- Plant-Based Options: Tofu and tempeh for vegetarians.
For high-protein meal prep ideas, check out High Protein Lunches for Work.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can knock you out of ketosis and should be avoided. These typically include high-carb, processed, and sugary items.
Sugary Snacks
- Candy, cakes, pastries, and soda are packed with refined sugars and offer no nutritional value.
- Replace with Keto-friendly desserts like sugar-free fat bombs or dark chocolate (85% cocoa or higher).
Find recipes for treats in Healthy Dessert Recipes with Macros.
Starchy Vegetables
These vegetables are high in carbs and should be avoided:
- Potatoes, sweet potatoes, yams, and parsnips.
- Corn and peas, which are also high in starch.
Balanced Keto Choices
By focusing on foods that are high in healthy fats, moderate in protein, and low in carbs, you can create delicious meals that keep you in ketosis. For a more comprehensive guide, explore Keto Diet Food Lists to build your weekly menu effectively.
Crafting a Simple Keto Meal Plan
Step 1: Calculate Your Macros
Use a Keto calculator to determine your ideal ratios of fats, proteins, and carbs based on your weight, activity level, and goals.
Step 2: Choose Your Recipes
Select recipes that align with your macros and include easy-to-prepare dishes for busy days.
Step 3: Plan Your Grocery List
Prepare a shopping list of Keto staples, including healthy fats, low-carb vegetables, and proteins.
Step 4: Meal Prep Strategies
Batch-cook proteins, pre-chop vegetables, and portion meals in advance to save time and stay consistent.
Sample Keto Meal Plan for Beginners
Breakfast Ideas
- Avocado and Egg Bowl: A combination of creamy avocado and poached eggs seasoned with salt and pepper.
- Keto Smoothie: Blend almond milk, spinach, chia seeds, and MCT oil for a nutrient-packed start to your day.
Lunch Suggestions
- Chicken Salad Wraps: Use romaine lettuce leaves as wraps and fill them with shredded chicken, avocado, and mayo.
- Zucchini Noodles with Pesto: Spiralized zucchini tossed in basil pesto and topped with grilled chicken or shrimp.
Dinner Options
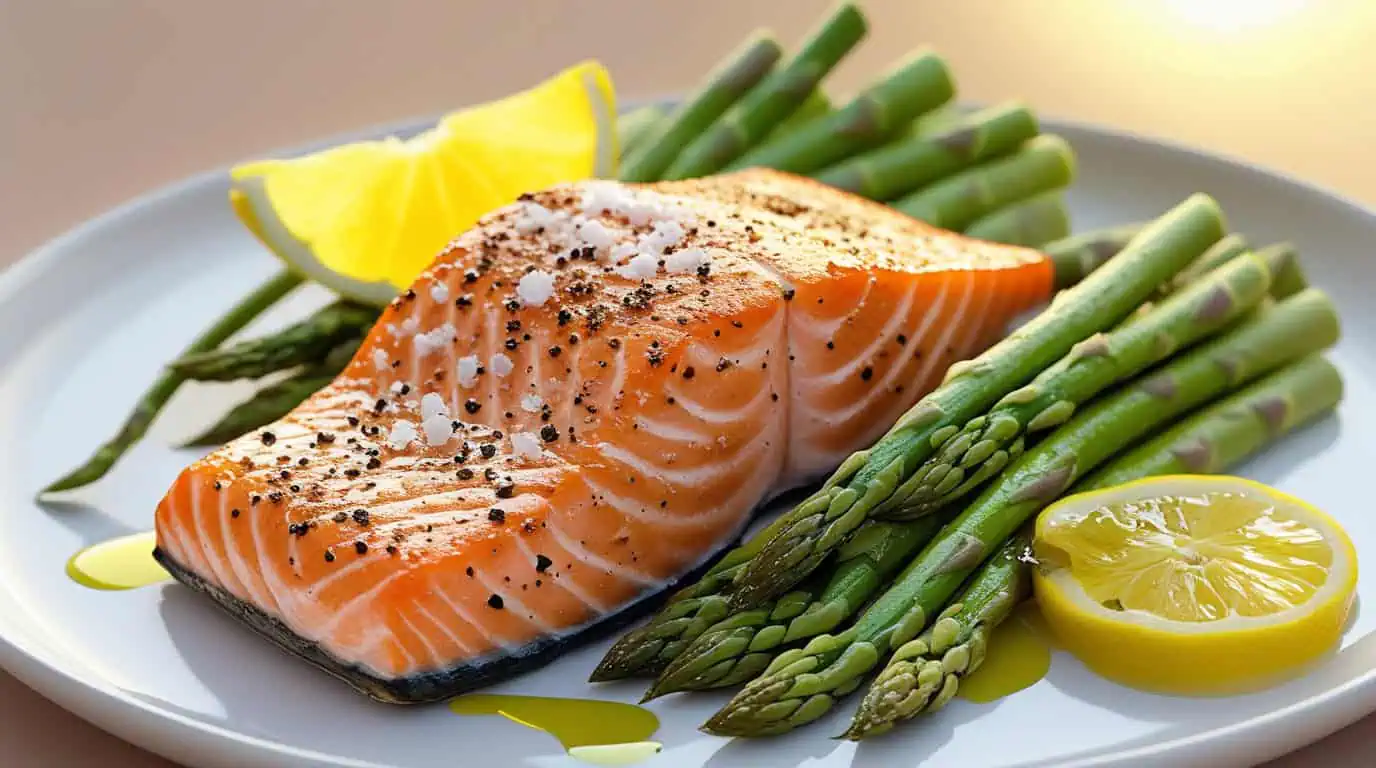
- Grilled Salmon with Asparagus: Serve with a drizzle of olive oil and lemon juice for a fresh, Keto-friendly dinner.
- Bunless Burgers: Layer beef patties with cheese, lettuce, tomato, and avocado for a satisfying meal.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Keto Flu: Symptoms and Solutions
Symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and irritability are common when starting Keto. Combat these by:
- Drinking plenty of water.
- Replenishing electrolytes with sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
Managing Cravings
To curb cravings:
- Keep Keto-friendly snacks like nuts, cheese, and dark chocolate on hand.
- Plan meals ahead to avoid hunger-driven decisions.
Dining Out on Keto
When dining out:
- Choose grilled proteins and low-carb sides like salads or steamed vegetables.
- Ask for sauces and dressings on the side to avoid hidden sugars.
FAQs About Keto Diet Meal Plans
Can I Follow Keto if I’m Vegetarian?
Yes! Focus on plant-based fats like avocado, coconut oil, and nuts, and include vegetarian proteins like tofu, tempeh, and seitan.
How Long Does It Take to Enter Ketosis?
Typically, it takes 2-4 days of strict carb restriction, though this varies based on your metabolism and activity levels.
What Are Common Side Effects of Keto?
Initial side effects may include fatigue, irritability, and digestive changes (commonly called “Keto flu”). These typically subside after the first week.
Can I Eat Fruits on Keto?
Yes, but only low-carb fruits like berries, in moderation, to avoid exceeding your carb limit.
Is the Keto Diet Safe for Everyone?
While generally safe, those with certain medical conditions (e.g., kidney disease) should consult a healthcare provider before starting.
How Do I Avoid Boredom with Keto Meals?
Incorporate variety by experimenting with different recipes, spices, and Keto-friendly international dishes.
Conclusion: Staying on Track with Keto
Sticking to the Keto diet requires preparation, consistency, and adaptability. By understanding the basics, planning your meals, and addressing challenges proactively, you can enjoy the numerous health benefits of this lifestyle. Whether your goal is weight loss, improved energy, or better mental clarity, the Keto diet offers a sustainable and effective path to success. Get started today with simple recipes and actionable tips to make Keto work for you!