Health Benefits of Alkaline Grains
What Are the Health Benefits of Alkaline Grains?
The health benefits of alkaline grains like quinoa, buckwheat, and oats are numerous and impactful. These grains are vital in promoting a balanced pH level, which is essential for overall wellness. You can enjoy improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and enhanced weight management by including them in your diet. The health benefits of alkaline grains also extend to better heart health, as their fiber and antioxidant content helps regulate cholesterol and combat oxidative stress. Incorporating these grains into meals allows you to experience alkaline grains’ full range of health benefits, making them a cornerstone of any balanced diet.
Table of Contents
What Are Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats?
Definition and Importance
Alkaline grains are foods that, when metabolized, help reduce acidity and maintain the body’s optimal pH balance. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Foods promoting alkalinity, such as quinoa, buckwheat, and oats, create an environment less prone to inflammation, disease, and digestive issues. These grains neutralize excess acidity caused by modern diets high in processed and acidic foods.
For a list of other healthy recipes to complement these grains, visit Healthy Meals for Breakfast.
How Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats Help Maintain pH Balance
A pH imbalance can lead to inflammation, fatigue, weakened immunity, and digestive discomfort. Alkaline grains like quinoa, buckwheat, and oats offer an easy, natural way to restore this balance. Their nutrient profiles make them essential additions to a healthy, well-rounded diet.
Quinoa: The Nutritional Powerhouse Among Alkaline Grains
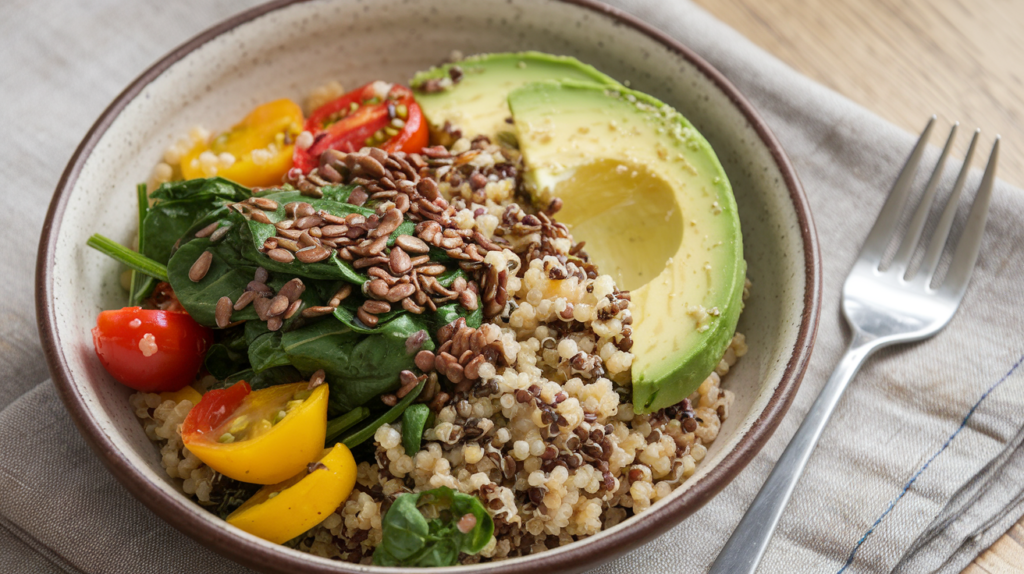

Introduction to Quinoa
Quinoa, often hailed as a “superfood,” is a nutrient-dense seed originating from the Andes Mountains of South America. Despite being classified botanically as a seed, it is commonly prepared and consumed as a grain, making it a staple in many alkaline diets. Its unique nutritional profile and versatility make it a powerful addition to meals focused on health and wellness.
Nutritional Profile of Quinoa
Quinoa is celebrated for its impressive nutrient composition, which includes:
- Complete Protein: Quinoa is one of the few plant-based foods that contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a vital protein source for vegetarians and vegans.
- Rich in Fiber: Its high fiber content aids digestion, promotes gut health, and supports weight management by keeping you full for longer.
- Essential Minerals:
- Magnesium: Crucial for muscle function and bone health.
- Potassium: Helps maintain a healthy pH balance and regulates blood pressure.
- Iron: Supports red blood cell production and oxygen transport.
- Zinc: Boosts immune function and aids in wound healing.
- Antioxidants: Contains flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol, which combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Health Benefits of Quinoa
- Promotes pH Balance: Quinoa’s alkaline-forming properties help reduce body acidity, creating an internal environment that minimizes inflammation and supports overall health.
- Supports Heart Health: Its fiber and antioxidant content contribute to lower cholesterol levels and protect against cardiovascular diseases.
- Enhances Digestive Health: High in dietary fiber, quinoa aids regular bowel movements and supports a healthy gut microbiome.
- Boosts Energy and Recovery: Quinoa’s complex carbohydrates and protein content provide sustained energy and aid muscle recovery, making it an excellent choice for active individuals.
- Manages Blood Sugar Levels: The low glycemic index of quinoa helps prevent blood sugar spikes, making it suitable for individuals with diabetes or those aiming for better glucose control.
Quinoa in Alkaline Diets
Quinoa’s alkaline nature complements modern diets by counteracting the acidity of processed and high-protein foods. Its nutritional richness allows it to serve as the foundation for a wide array of recipes, from breakfast porridges to hearty salads.
Cooking and Preparation Tips

- Rinse Thoroughly: Wash quinoa before cooking to remove its natural coating, saponin, which can have a bitter taste.
- Cook to Perfection: Use a 2:1 water-to-quinoa ratio and simmer for about 15 minutes until the grains are tender and translucent.
- Enhance Flavor: Toast quinoa in a dry pan before boiling to enhance its nutty flavor.
- Versatility: Use quinoa as a base for salads, soups, stir-fries, or breakfast bowls.
Recipe Ideas
- Quinoa Salad with Avocado and Berries: Combine cooked quinoa with fresh spinach, avocado slices, and a medley of berries, topped with a light lemon vinaigrette.
- Quinoa Breakfast Porridge: Cook quinoa in almond milk and sweeten with honey or maple syrup. Add nuts, seeds, and fresh fruit for a wholesome start to your day.
- Quinoa-Stuffed Bell Peppers: Mix quinoa with vegetables, herbs, and spices, then bake in hollowed-out bell peppers for a filling and nutritious dinner.
Quinoa stands out as a nutritional powerhouse among alkaline grains, offering an unparalleled combination of health benefits and culinary versatility. By incorporating quinoa into your diet, you can promote a balanced pH, support digestive health, and enjoy a wide array of delicious and nutrient-packed meals. Whether you’re seeking to improve your overall wellness or enhance your culinary repertoire, quinoa is an invaluable addition to any lifestyle.
Buckwheat: A Heart-Healthy Alkaline Grain
What Is Buckwheat?
Despite its name, buckwheat is naturally gluten-free and not related to wheat. It is a pseudo-grain harvested from the seeds of the Fagopyrum esculentum plant and is widely used in Eastern European and Asian cuisines.
Nutritional Profile
Buckwheat is packed with antioxidants, protein, and fiber, making it a valuable addition to an alkaline diet.
- Rutin: A potent antioxidant that strengthens blood vessels and improves circulation.
- Magnesium and Manganese: Essential minerals for muscle and bone health.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Provide sustained energy without spiking blood sugar levels.
Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Buckwheat’s ability to reduce inflammation stems from its high concentration of rutin and other phytonutrients. Regular consumption can help alleviate arthritis symptoms, lower the risk of heart disease, and combat oxidative stress.
How to Use Buckwheat
Buckwheat can be incorporated into both sweet and savory dishes. It is commonly used in pancakes, salads, stir-fries, and porridge. For creative ideas, visit Easy Breakfast Casserole Recipe.
Oats: The Versatile and Alkalizing Grain
What Are Oats?
Oats are one of the most widely consumed grains globally. Known for their high fiber content, they are particularly effective in promoting heart health and supporting digestion.
Nutritional Value
Oats are a rich source of beta-glucan, a soluble fiber that lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. They also contain essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, such as avenanthramides, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
How Oats Promote Alkalinity
While oats are mildly acidic in raw form, they are considered alkaline-forming after digestion. Their high fiber content supports gut health, helping regulate the digestive tract’s pH balance.
Recipe Ideas
For maximum nutrition, use steel-cut or rolled oats rather than instant oats. Create delicious breakfast bowls by topping cooked oats with fresh fruits, nuts, and seeds. For savory options, consider using oats in veggie burgers or soups as a binder. Explore more ideas in Sausage Breakfast Ideas.
How Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats Improve Digestive Health
The Role of Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats in Reducing Inflammation
The high fiber content in quinoa, buckwheat, and oats promotes regular bowel movements, preventing constipation and supporting healthy gut bacteria. The soluble fiber in oats and quinoa softens stool, while the insoluble fiber in buckwheat adds bulk and aids intestinal movement.
Impact on Gut Microbiome
Alkaline grains help balance the gut microbiome by fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria. This contributes to improved digestion, better nutrient absorption, and reduced inflammation.
Weight Management with Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats
Satiety and Appetite Control
Alkaline grains are ideal for weight management because they keep you full for longer. The fiber in quinoa, buckwheat, and oats slows digestion, reduces hunger pangs, and prevents overeating.
Low-calorie, High-Nutrition Foods
These grains are nutrient-dense yet low in calories, making them excellent choices for those seeking to manage or lose weight without sacrificing nutrition.
For low-calorie recipe ideas, check out Healthy Lunch Ideas for Weight Loss.
Alkaline Grains and Inflammation
How Acidity Impacts Inflammation
An acidic internal environment can exacerbate inflammation, leading to chronic conditions like arthritis and cardiovascular disease. Alkaline grains help neutralize acidity, reducing inflammatory markers in the body.
Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
- Quinoa: Contains flavonoids that combat oxidative stress.
- Buckwheat: Rich in rutin, which reduces inflammation and strengthens capillaries.
- Oats: Provide avenanthramides, which are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Cooking Tips for Alkaline Grains: Best Practices and Nutrient Retention
Alkaline grains such as quinoa, buckwheat, and oats are versatile and nutrient-dense ingredients that require careful preparation to maximize their flavor, texture, and health benefits. Here are detailed tips for cooking and handling these grains to make the most of their nutritional profiles.
Best Practices for Cooking Alkaline Grains

Quinoa:
- Rinse Thoroughly:
- Quinoa has a natural coating called saponin, which can impart a bitter taste if not removed. Rinse quinoa under cold running water in a fine-mesh sieve until the water runs clear.
- Optimal Water Ratio:
- Use a 2:1 ratio of water to quinoa. For every one cup of quinoa, use two cups of water or broth for enhanced flavor.
- Cooking Time:
- Bring the water to a boil, reduce the heat to low, cover the pot, and simmer for about 15 minutes or until the water is fully absorbed and the quinoa appears light and fluffy.
- Fluff with a Fork:
- After cooking, let the quinoa sit covered for 5 minutes, then fluff it with a fork to separate the grains and enhance its texture.
- Enhance Flavor:
- Toast quinoa in a dry skillet over medium heat for 3-5 minutes before cooking to bring out its nutty flavor.
Buckwheat:
- Toast Before Cooking:
- Toasting buckwheat groats in a dry pan enhances their nutty aroma and improves their texture, making them less mushy when cooked.
- Water Ratio:
- Use a 2:1 water-to-buckwheat ratio for light, fluffy groats. For a softer texture, slightly increase the water.
- Cooking Time:
- Add buckwheat to boiling water, reduce the heat, and simmer uncovered for about 10-15 minutes. Drain any excess water.
- Optional Soaking:
- For better digestibility and quicker cooking, soak buckwheat in water for 30 minutes before cooking.
- Seasoning:
- Add a pinch of salt or spices like cinnamon or turmeric during cooking, depending on the recipe.
Oats:
- Overnight Soaking:
- For a creamy and digestible texture, soak oats overnight in water, plant-based milk, or yogurt. Overnight oats are especially suitable for quick breakfasts.
- Cooking Liquid:
- Use water, almond milk, oat milk, or a mix of milk and water to cook oats. This enhances their creaminess and nutritional content.
- Cooking Time:
- Steel-cut oats: Simmer for 20-30 minutes for a chewy texture.
- Rolled oats: Cook for 5-10 minutes for a soft and creamy consistency.
- Instant oats: Ready in 1-2 minutes but lower in texture and nutrition.
- Flavor Enhancements:
- Add a pinch of salt, cinnamon, or vanilla extract during cooking. Top with fruits, nuts, seeds, or honey for added flavor and nutrition.
Maximizing Nutrient Retention
- Avoid Overcooking:
- Overcooking can lead to the breakdown of essential nutrients. Cook grains just until tender, as prolonged heat can degrade vitamins and antioxidants.
- Use Gentle Cooking Methods:
- Steaming: Retains nutrients better than boiling, particularly for grains used in salads or side dishes.
- Boiling: Effective for grains but ensure the water-to-grain ratio is correct to avoid nutrient loss.
- Soaking: Presoaking grains reduces cooking time, preserves nutrients, and increases digestibility by neutralizing phytic acid.
- Minimal Draining:
- When cooking grains that require draining (e.g., excess water for buckwheat), use the minimum amount of water necessary to reduce nutrient loss.
- Flavor with Care:
- Use natural seasonings like herbs, lemon zest, or vegetable broth to enhance flavor without adding excessive salt or processed additives.
Tips for Serving Alkaline Grains

- Combine with Alkaline Foods: Pair grains with vegetables, avocado, or nuts to boost their alkalizing effects.
- Batch Cooking: Cook larger portions of grains and store them in airtight containers for up to 5 days in the refrigerator.
- Freezing: Cooked grains freeze well for up to 3 months, making meal prep more efficient.
By following these practices, you can enjoy the full flavor, texture, and health benefits of alkaline grains like quinoa, buckwheat, and oats while preserving their valuable nutrients.
FAQs: Understanding Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats
What are the health benefits of alkaline grains and Quinoa Buckwheat Oats?
These grains help maintain pH balance, support digestion, reduce inflammation, and promote weight management. They are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential nutrients.
Can You Eat Alkaline Grains Every Day?
Daily consumption of quinoa, buckwheat, and oats is beneficial for overall health.
Are Alkaline Grains Gluten-Free?
Yes, all three grains are naturally gluten-free, making them safe for individuals with gluten intolerance.
How Do Alkaline Grains Aid Detoxification?
Their high fiber content supports regular bowel movements, eliminating toxins and maintaining a healthy internal environment.
What are the best recipes for using alkaline grains?
Explore quinoa salads, buckwheat pancakes, and oat-based smoothies for delicious ways to incorporate these grains into your diet.
Conclusion: Embracing Alkaline Grains Quinoa Buckwheat Oats for Healthier Living
Incorporating quinoa, buckwheat, and oats into your daily meals offers numerous health benefits, from maintaining pH balance to supporting digestion, reducing inflammation, and aiding in weight management. Their versatility and nutrient density make them essential to a balanced, healthy diet. Explore more recipes and tips at Fabulous Taste. Making these grains a regular part of your diet takes a significant step toward a healthier, more vibrant life.





